-
The Foundations: Logic and Proofs (1)수학/이산수학 2020. 3. 30. 14:06
Logical Operators
- Propositional variables
: Variables that represent propositions 변수가 명제를 표현한다.
: p, q, r, s ...
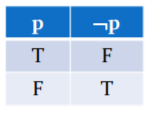
- Negation : ~p
대표적인 unary operator
- Congunction (AND) : p∧q
: binary operator
: 첫번째 row와 두번째 row가 동시에 일어날 수 없다. -> q가 동시 T ,F 라는 의미이기 때문이다.
: truth table의 크기는 operand의 갯수로 나타낼수 있다. (2^n)

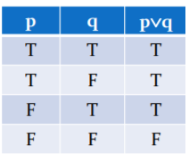
- Disjunction (OR) : p∨q
- Exclusive (XOR) : pⓧq

Conditional Statements

- If p, then q
- p -> q
- p: hypothesis( or antecedent)
- q: conclusion( or consequence)
- Converse : q -> p 역
- Inverse : ~p -> ~q 이
- Contrapositive : ~q -> ~p 대우
: A conditional statement and its contrapositive are equivalent
* 대우의 진리표는 원래의 Conditional Statements와 같다.
* hypothesis가 F면 결론은 중요하지 않다. 상관없이 T다.
왜? 전제가 틀렸으니깐 그냥 그렇기 보기로 한것으로 볼 수 있다.
Biconditional Statement

- p if and only if q
- p <-> q
- p iff q
* p이면 q 이고, q이면 p이다.
* 진리표는 (p->q) ∧ (q->p) 계산하면 나온다.
* p->q ≡ ~q -> ~p
≡ ~p ∨ q
Logical Equivalences 동치
- p ≡ q : compound propositions p and q are called logically equivalent if p<->q is a tautology
- p->q ≡ ~p ∨ q

Precedence of Operators

* 헷갈릴땐 무조건 괄호사용해서 명확히 할것!
Consistence of Rules
- If the rules are not consistent, there is no way to satisfy all rules together
* Rules = > compound proposition :변수가 1개이상
변수 1개이상이 무조건 나열될수 없다.(p q) -> 1개 이상인 변수는 operator로 묶여졌잇다. (p∨ q)
- Consistence : 어떤 world, 조건에서 동시에 T가 만족하는 world,조건가 있어야 consistence가 만족
{ p∨q, ~p, p->q } -> consistence
{ p∧q, ~p, p->q } -> 이 3개의 rule은 consistence 하지 않다

* Logical Equivalences 와 Consistence of Rules 차이?
Consistence of Rules는 최소 하나의 world 에서 T이면 된다. T,F의 의미가 중요.
Logical Equivalences 는 T,F 자체의 의미에 상관없이 어떤 world에서 그냥 always 같으면 결과가 나오면된다.
Logic and Bit Operations

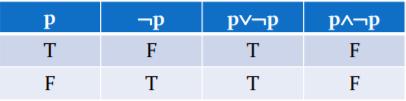
Tautology and Contradiction
Tautology
- A compound proposition that is always true
Contradiction
- A compound proposition that is always false
Contingency
- A compound proposition that is neither a tautology nor a contradiction -> 가장 평범
Constructing New Logical Equivalences
: 풀이의 편이를 위해 식 약간 변형하는 것 - 결과 영향 x
- Show that ~ (p->q) and p ∧~ q are logically equivalent
~ (p->q) ≡ ~ (~p∨ q)
≡ ~ (~p)∧ ~q by De Morgan law
≡ p ∧ ~q by double negation law
- Show that (p∧q) -> (p∨q) is a tautology
(p∧q) -> (p∨q) ≡ ~(p∧q) ∨ (p∨q)
≡ (~p∨~q) ∨ (p∨q) by De Morgan law
≡ (~p∨p) ∨ (~q∨q) by associative and commutative laws
≡ T ∨ T by negation law
≡ T by domination law
'수학 > 이산수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
The Foundations: Logic and Proofs (2) (0) 2020.04.06